Exploring Life After Death: Researchers Discover New Life Forms Emerging from Dead Cells
Whereas life and death have been the two opposing forces for centuries, new discoveries bring people to their senses that there is actually a “third state” between life and death in which some dead organism’s cells are functioning and which even can transform into new forms of life. These findings that nothing is impossible in biology are broadening the bounds of such thoughts regarding this field and opening the doors for such innovations in regenerative medicine, organ donation, or cellular research.
The Third State: Life After Death
“Researchers Explore Life After Death was traditionally understood by most as the irreversible cessation of all biological functions in an organism. Recent research, however, has shown that there are cells which can live on to become even developed into new functions following the death of the organism. This brought up a “third state” in which life and “Researchers Explore Life After Death blur into one another, giving rise to entirely new forms of life from what was otherwise believed to be dead.
In many ways, this concept is reminiscent of the process of metamorphosis. Just like a caterpillar turns into a butterfly or a tadpole into a frog, these post-mortem transformations of cells challenge the set and fixed concept of life and death. When cells are derived from dead organisms under certain conditions, they can reorganize, function, and create shapes and behaviors that move beyond the original biological purposes of their origination.
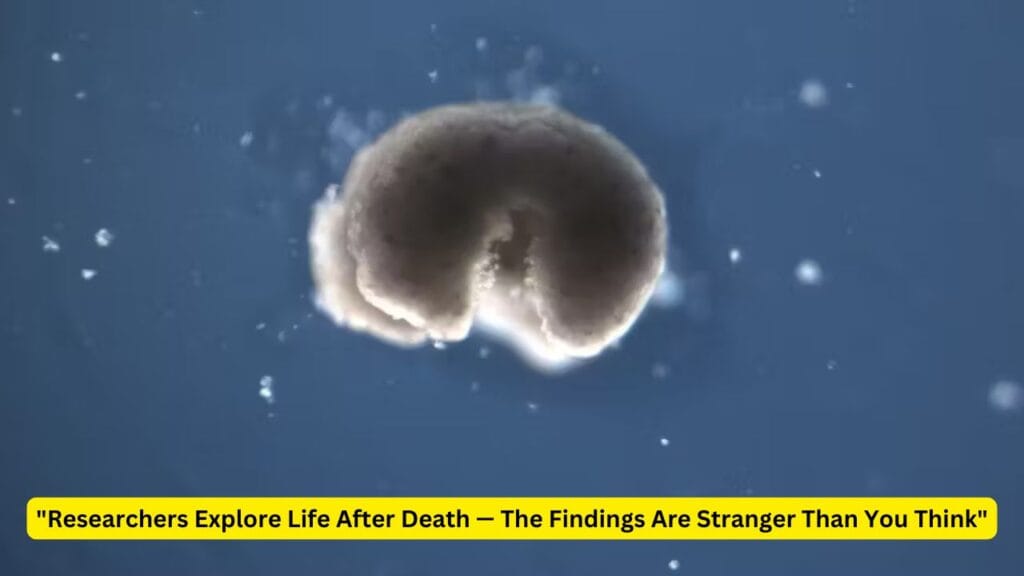
Xenobots: Life from Dead Cells
Perhaps the most impressive feature of this third state is that of xenobots. These life forms, derived from the skin cells of deceased frog embryos, spontaneously rearranged themselves into multicellular organisms in the laboratory. This is more remarkable regarding xenobots because they are moving entities able to navigate their environment by using a tiny hair-like structure called cilia, which is primarily meant for mucus movement in living frogs. However, in xenobots, the cilia are used to propel, move forward, and even perform self-replication, a method where they physically replicate their structure without growing.
This is “Researchers Explore Life After Death also an interesting example on how, even in the post-mortem state, cells can change into entirely new forms of life with new functions. In contrast to traditional cell replication involving growth, xenobots can replicate by restructuring their framework, a process that disregards our conventional understanding of biology.
Anthrobots: A New Class of Multicellular Organisms
In addition to xenobots, researchers have also created anthrobots—multicellular organisms made from human lung cells. These anthrobots can move through their environment and even repair themselves and other cells, including injured neurons. This is exciting as it intimates that human cells—even ones taken a”Researchers Explore Life After Death—can reorganize into complex, functionally responsive life forms.
These anthrobots are quite promising in regenerative medicine because it would be possible to engineer human cells into self-replicating, self-repairing organisms, providing novel treatments for many conditions, such as tissue regeneration or targeted drug delivery without triggering immune rejection.
What Makes Cells Continue to Live After Death?
So, “Researchers Explore Life After Death what allows cells to survive and function after the organism has died? Several factors contribute to this postmortem resilience, including environmental conditions, metabolic activity, and preservation techniques.
Different types of “Researchers Explore Life After Death cells have varying levels of survival after death. For instance, human white blood cells may survive for up to 60 to 86 hours post-mortem, while skeletal muscle cells in mice can regenerate for up to 14 days. Some cells, such as fibroblasts from sheep and goats, can even be cultured for up to a month after death.
“Researchers Explore Life After Death 2024
Metabolic activity is a major factor about whether cells can survive post-mortem. Cells that make high energy demands in order to perform require a higher energy supply compared to cells that have low energy needs. That is why preservation techniques, especially cryopreservation, can be very crucial in terms of the maintenance of cellular function because it will retain its metabolic activity and avoid the breakdown of its tissues.
“Researchers Explore Life After Death have discovered that a number of genes associated with stress and the immune system are activated post-mortem, which may allow cells to survive better under the conditions of disrupted homeostasis and survive longer. However, the cells’ ability to survive and transform is greatly influenced by such factors as age, health, and time after death.
Medicine and the Promise of Post-Mortem Cellular Transformation
The “Researchers Explore Life After Death discovery of the “third state” has far-reaching implications for biology and medicine. The knowledge of cells’ ability to function persistently after death can be crucial in new treatments of medical conditions.
For instance, anthrobots may be applied in the drug delivery to patients by bypassing the immune response to a foreign tissue. These cells may be applied to treat diseases such as atherosclerosis by clearing the arterial plaque or even by assisting cystic fibrosis patients by removing excess mucus from the lung.
Even more remarkable is that these organisms have a finite lifespan; they spontaneously degenerate after four to six weeks, acting like a “kill switch” to prevent uncontrolled growth and ensuring they are not a threat to the patient.
This “Researchers Explore Life After Death may be revolutionized in the field of personalized medicine, where new, customizable treatments are given to patients. Researchers also believe that biodegradable tissues will help in replacing damaged organs or regenerating tissue without the chance of rejections, providing a solution for saving life by providing transplants to those who need them.
Life After Death-The Future
As “Researchers Explore Life After Death science explores the “third state,” we will surely find many things even more astonishing than that by the development of plastic cells with diverse capacities and their right to adapt and transform beyond the original functions. It may be said that the behavior after death will be studied to gain revolutionary medical breakthroughs both in cell therapy and in organ regeneration.
Although it is still in its infancy, there are enormous potential treatments and scientific advances emerging from a newly refurbished understanding of post-mortem cellular behavior. Researchers are now pursuing studies of this fascinating area of research, promising to advance our appreciation of life, death, and everything in between.
Conclusion
This “Researchers Explore Life After Death discovery of new life forms coming out from dead cells challenges our old conceptualizations about life and death. Through pioneering research, scientists identified a “third state” in which cells remain viable, responsive, and changing even after the death of an organism. From xenobots to anthrobots, these concepts have the “Researchers Explore Life After Death potential to introduce a new revolution in regenerative medicine, through personalized treatments and even in organ transplants. Much is yet to be discovered, but these research outcomes already point to an interesting future for cellular science.
FAQs
1.What is the “third state” for life and death?
- The “third state” is the post-mortem state, in which certain cells maintain functions and may even become new forms of life that blur the old distinctions of life versus death.
2.How do xenobots self-replicate?
- Xenobots reproduce through the remodeling of its morphology, rather than growing. They use their cilia to move and replicate their outline in a procedure that is not like traditional cell reproduction.
3.Can human cells live beyond death?
- Yes, “Researchers Explore Life After Death a type of human cells, like lung cells, have been demonstrated to survive after death and reorganize into multicellular organisms capable of self-repair and movement.
4.Medical applications for the “third state”:
What are they?
This may open up new treatment possibilities for drug delivery, and tissue or even organ replacement
without immune rejection.
5.How can cryopreservation help cells survive after death?
- Cryopreservation slows down cellular metabolism and prevents the breakdown of tissues, helping cells maintain their function for longer periods post-mortem.